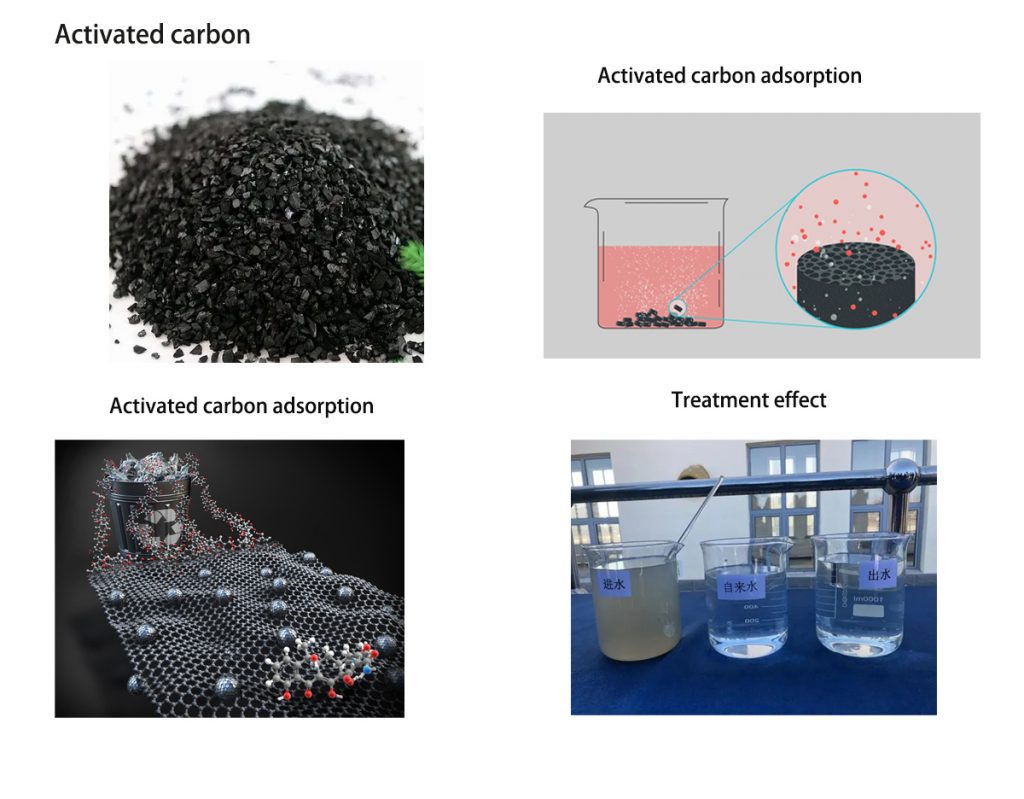
The active adsorption system in sewage treatment is a treatment method that uses adsorbents such as activated carbon to remove pollutants from water. Activated carbon is a carbon material with a highly developed pore structure and a huge specific surface area, which has strong adsorption capacity for many organic compounds, colloids, microorganisms, etc. Therefore, active adsorption systems are widely used in wastewater treatment, mainly for removing pollutants such as organic matter, chromaticity, odor, and heavy metal ions from water.
The working principle of an active adsorption system is to adsorb pollutants from water onto its surface through the adsorption effect of activated carbon, thereby achieving the removal of pollutants. The adsorption process of activated carbon is a combination of physical adsorption and chemical adsorption. It can be achieved through physical adsorption using the macropores and mesopores on the surface of activated carbon, as well as chemical adsorption using the functional groups on the surface of activated carbon.
In an active adsorption system, factors such as the selection, dosage, and adsorption time of activated carbon can affect the adsorption effect. Generally speaking, the selection of activated carbon should be comprehensively considered based on factors such as water quality characteristics, treatment objectives, and economy. The dosage should be determined based on factors such as the concentration of water pollutants and the adsorption performance of activated carbon. The adsorption time should be adjusted according to the actual situation to achieve the best adsorption effect