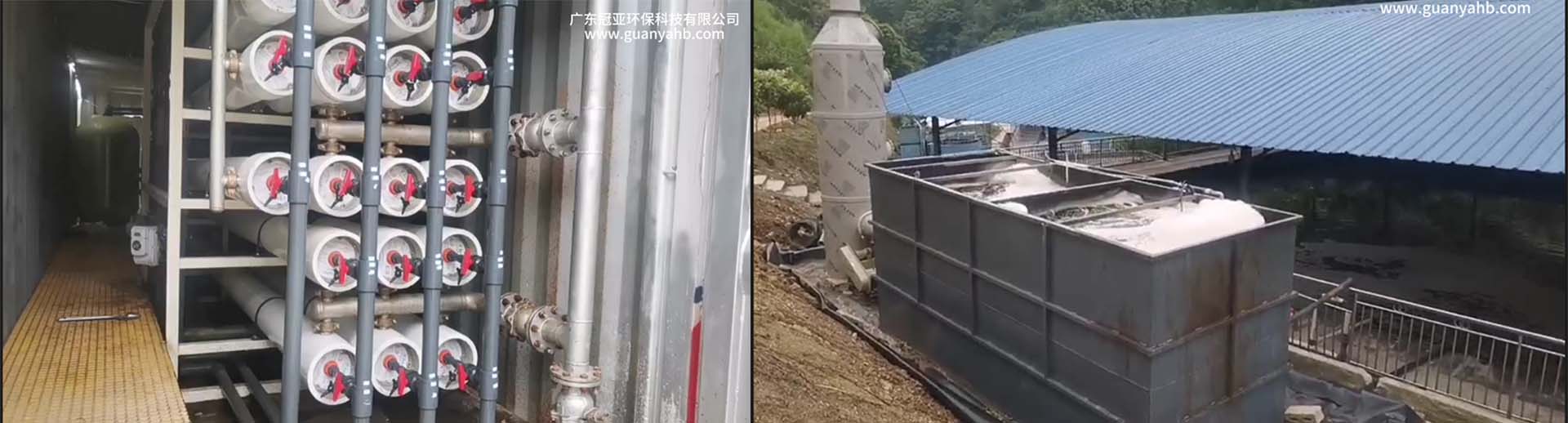
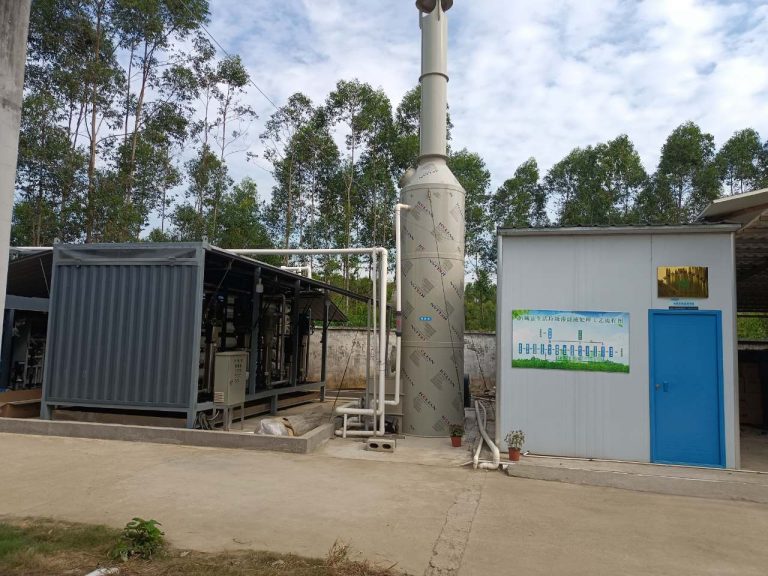
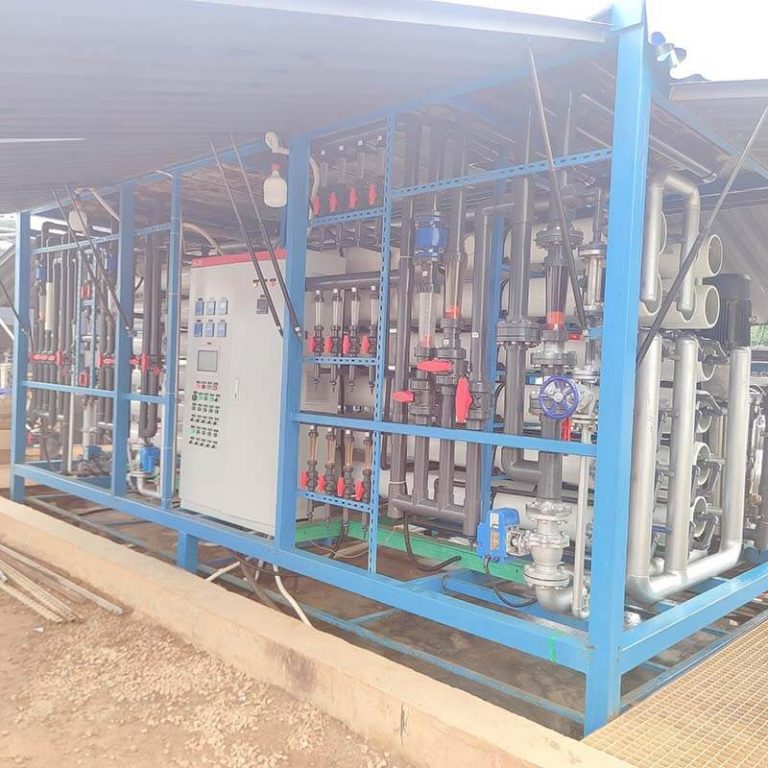
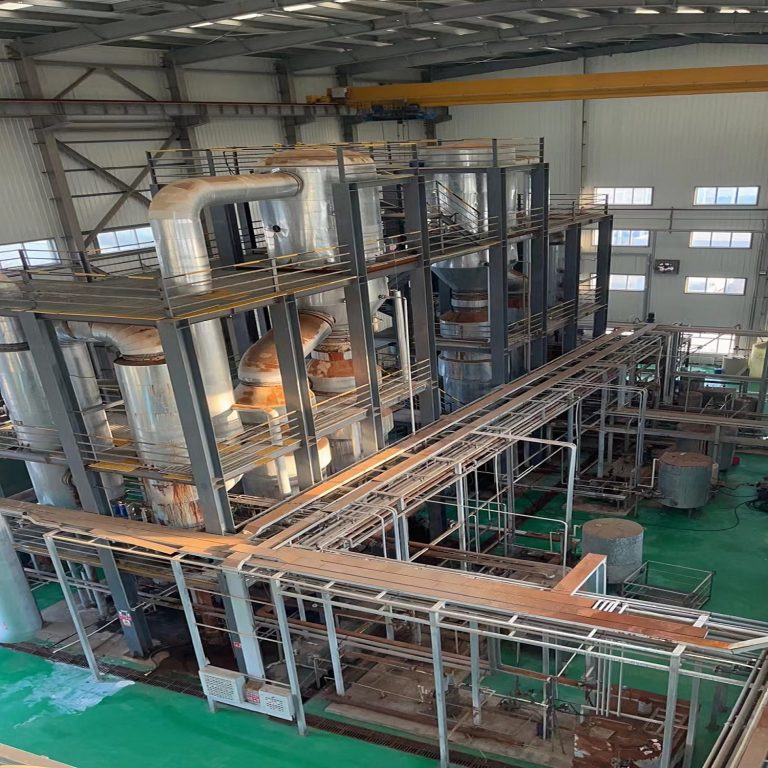
The real project site for the leatchate sewage treatment equipment located at Pingtan district.
The requirements for achieving standard leachate treatment mainly include the following aspects:
1. Preprocessing
Removing suspended solids: Removing suspended particles from leachate through physical methods (such as precipitation, filtration) or chemical methods (such as coagulation, flocculation) to reduce the load on subsequent treatment units.
Adjusting water quality: By adding chemical agents (such as acids and bases) or using biological methods (such as aeration) to adjust the pH value, nutrient concentration, and other water quality indicators of the leachate, in order to meet the requirements of subsequent treatment units.
Removing organic matter: Removing organic matter from leachate through biological methods (such as aerobic or anaerobic biological treatment) or chemical methods (such as oxidation and reduction) to reduce its pollution to the environment.
2. Biochemical treatment
Aerobic biological treatment: Utilizing aerobic microorganisms (such as activated sludge) to decompose organic matter in leachate into carbon dioxide and water under aerobic conditions, while removing nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus.
Anaerobic biological treatment: using anaerobic microorganisms (such as methanogens) to decompose organic matter in leachate into methane and carbon dioxide under anaerobic conditions, while removing some nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus.
3. Deep processing
Membrane separation technology: using membrane separation technologies such as ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, or reverse osmosis to further remove pollutants such as organic matter, inorganic salts, and heavy metals from the leachate, in order to achieve higher emission standards.
-Advanced oxidation technology: using strong oxidants such as ozone, hydrogen peroxide, or Fenton reagent to oxidize recalcitrant organic matter in leachate into small molecular substances for subsequent removal by treatment units.
4. Disinfection
Disinfectant disinfection: Disinfectants such as chlorine gas, sodium hypochlorite, or chlorine dioxide are used to disinfect the treated leachate to kill pathogenic microorganisms.
Ultraviolet disinfection: Using ultraviolet radiation to disinfect the treated leachate to kill pathogenic microorganisms.
5. Sludge treatment
Sludge concentration: The sludge generated during the biochemical treatment process is concentrated using methods such as gravity concentration, air flotation concentration, or centrifugal concentration to reduce the load on subsequent treatment units.
Sludge dewatering: The concentrated sludge is dehydrated using equipment such as belt filter press, plate and frame filter press, or centrifuge to reduce its volume and subsequent processing costs.
Sludge disposal: Disposal of dehydrated sludge through methods such as landfilling, incineration, or resource utilization to avoid secondary pollution to the environment.
We are professional waste water treatment factory and we can do customized solution according to the raw water situation. welcome to contact us for more information.