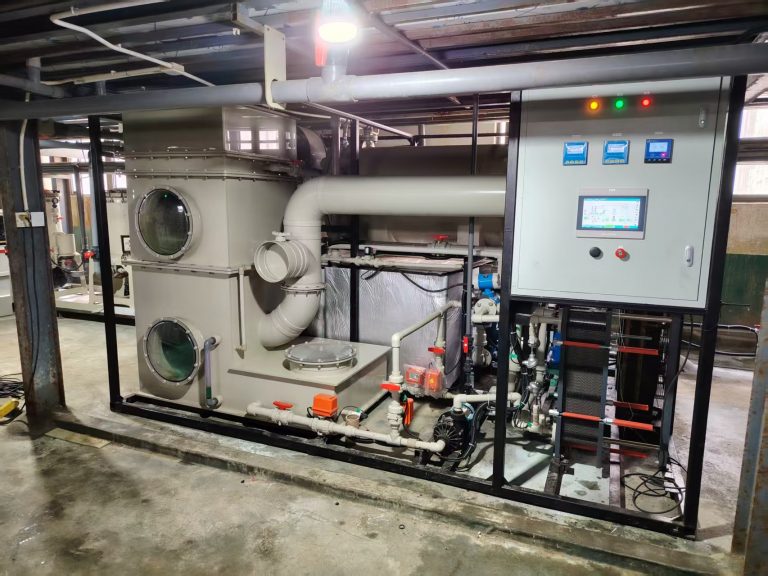
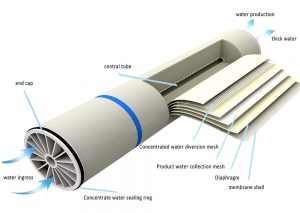
Let’s explain what is Reverse Osmosis (RO)?
RO is a process of transferring solutes from high concentration areas to low concentration areas in a solution through a semi permeable membrane. It is a commonly used water treatment technology that can effectively remove impurities such as dissolved solids, dissolved gases, and microorganisms from water, resulting in purified water. At present, the reverse osmosis technology is widely used is our lift such as the drinking water treatment, water treatment for food/beverage etc.
Main performance parameters of reverse osmosis
1) Water permeability. It refers to the amount of water passing through unit membrane area per unit time. It mainly depends on factors such as the material and structure of the membrane, but the water permeability of a certain reverse osmosis membrane depends on the operating conditions;
- The water permeability increases with the increase of temperature and increases proportionally with the increase of working pressure;
- The water permeability decreases with the increase of the inlet water concentration;
- The water permeability decreases with the increase of the recovery rate.
2) Recovery rate. The conversion rate of water supply to permeate directly affects the cost of the desalination system. The recovery rate for bitter brine is approximately 90%; the recovery rate for high-bitter brine is 60%-65%; and the recovery rate for industrial seawater systems is 35%-45%.
3) Membrane flux. It indicates the velocity of water flowing through a specific area of the membrane surface.
For surface water, it is 8GFD-14GFD (13L/m3h-23L/m3h); for reverse osmosis water, it is 14GFD-18GFD (23L/m3h—30L/m3•h); for seawater, it is 7GFD-8GFQ.
The operating conditions of reverse osmosis device
In order to ensure the safe and reliable operation of reverse osmosis device, it is very necessary to select certain suitable operating conditions. The main operating conditions of reverse osmosis device are inlet pH value, inlet temperature and operating pressure.
1) Inlet pH value: When cellulose acetate membrane is running, water should be slightly acidic, and the pH value is generally controlled between 4 and 7. Outside this range, the hydrolysis and aging of the membrane are accelerated. It is currently believed that the pH value is between 5-6. The hydrolysis of the membrane will not only cause a decrease in water production, but also cause the membrane’s ability to remove salt to continue to decrease until the membrane is damaged.
2) The inlet temperature: The inlet temperature has a certain effect on the water production. When the temperature increases by 1 degree Celsius, the water permeability of the membrane increases by about 2.7%. The lower limit of the inlet temperature of the reverse osmosis membrane is 5c-8C, and the percolation rate is very slow at this time. When the temperature rises from 11 degrees Celsius to 25 degrees Celsius, the water production increases by 50%. However, when the temperature is higher than 30C, most membranes become unstable, accelerating the rate of hydrolysis. Generally, the maximum temperature for the operation and storage of cellulose acetate membrane is 35°C, and it is advisable to control it between 25°C and 35°C.
3) Operating pressure. The osmotic pressure is proportional to the salt content in the raw water and has nothing to do with the membrane. When the operating pressure is increased, the membrane is compacted, the salt permeability will decrease, the water permeability will increase, and the water recovery rate will be improved. However, when the pressure exceeds a certain limit, it will cause the membrane to age, the deformation of the membrane will increase, and the water permeability will decrease.